Blog Layout
The Use of Air Arc Gouging
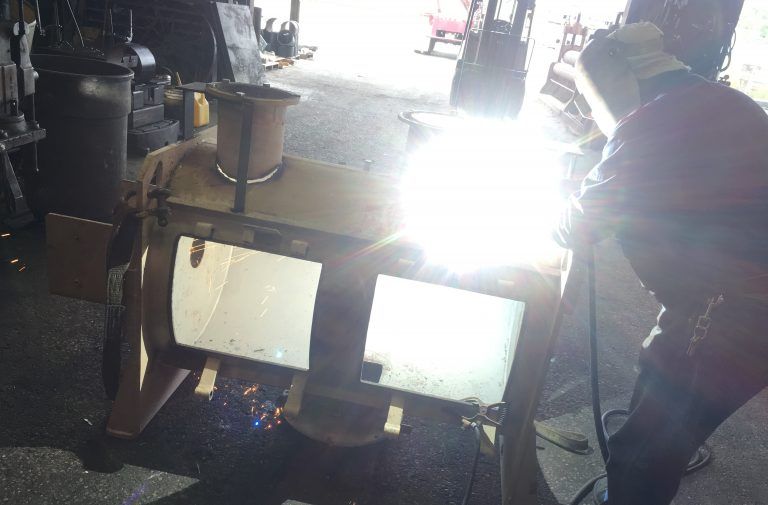

Air arc gouging is a process of removing metal by using heat generated from a carbon arc. This process utilizes a carbon/graphite electrode, compressed air and a standard power source. The extreme heat arc created between the electrode and a metal workpiece gouges and melts the workpiece. The compressed air also blows away the molten metal. This process is common for cutting stainless steel, carbon steel and alloys of copper, brass, aluminum and magnesium.
Air Arc Gouging
The Purpose of Air Arc Gouging
The main goal of air arc gouging is to remove defective or old welds to repair or dismantle equipment. Unlike oxy-fuel cutting, air arc gouging avoids the need for oxidation of the metal to cut.
The rate of metal removal depends on the efficiency of air jet in removing molten metal and the melting rate.
How Air Arc Gouging Works
Gouging commences by striking the electrode tip on the workpiece surface to initiate the arc. The manual metal arc (MMA) welding electrode tips are withdrawn. However, the electrode tips are not withdrawn to establish the arc length. The air stream immediately blows away the molten metal directly under the electrode tip (arc). It is essential that the air stream is toward the arc from behind the electrode and sweeps under the tip of the electrode for effective metal removal. The diameter of the electrode determines the width of the groove.
However, the angle of the electrode to the workpiece and rate of travel dictates the depth. Relatively high travel speeds are a possibility when using a low electrode angle. This produces a shallow groove. A steep angle will result in a deep groove and requires slower travel speed. Keep in mind, a steeply angled electrode may give rise to carbon contamination.
Gouging Width
You can increase the gouging width significantly by oscillating the electrode in a circular or restrictive weave motion during gouging. This is helpful for removing a weld or plate imperfection that is wider than the electrode itself. However, it is critical that weave width does not exceed four times the diameter of the electrode. The groove surface needs to be relatively free of oxidized metal and is ready for welding without further preparation. If a carbon rich layer forms, then dressing by grinding the side-walls of the gouge carries out. In addition, dressing by grinding or another approved method will be necessary if working on crack-sensitive material such as high strength, low alloy steel.
Benefits of Air Arc Gouging
Some of the many benefits of air arc gouging include the following:
- Besides being common for cutting metals and gouging defective metal, this process is common for preparing welding grooves and removing old damage welds as well. The main advantage of this technique is that the temperature of the surrounding area of the cut material does not reach the maximum as the metal is quickly removed after melting.
- You can perform this process on the workpiece at all positions.
- Air arc gouging can gouge or cut almost all common metals.
- Cleaning is necessary when performing air arc gouging for the weld preparation of zirconium, titanium and stainless steel as there’s removal of most of the surface carbonized materials near the cut during cleaning. You can cut these materials with this process to form scraps that you can re-melt.
These just the basics about the use of air arc gouging. Don’t hesitate to contact Brazos Industries with the link below for more information!
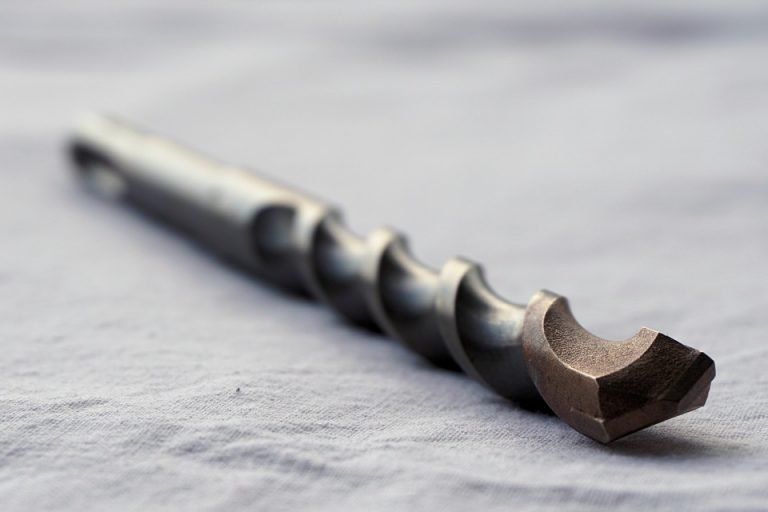

July 16, 2017
Many are unaware that drill bits require regular sharpening to give their best service. Similar to knives and axes, a dull drill bit requires much more force to do the same job. Instead of wearing the user out, a dull drill bit will inevitably wear out your drill. Giving your drill bits regular spot sharpening with a file is the best way to protect your investment in high-quality power tools. Brazos Industries knows the importance of properly sharpening drill bits, and we would like to share with you how to sharpen drill bits to protect your investment.
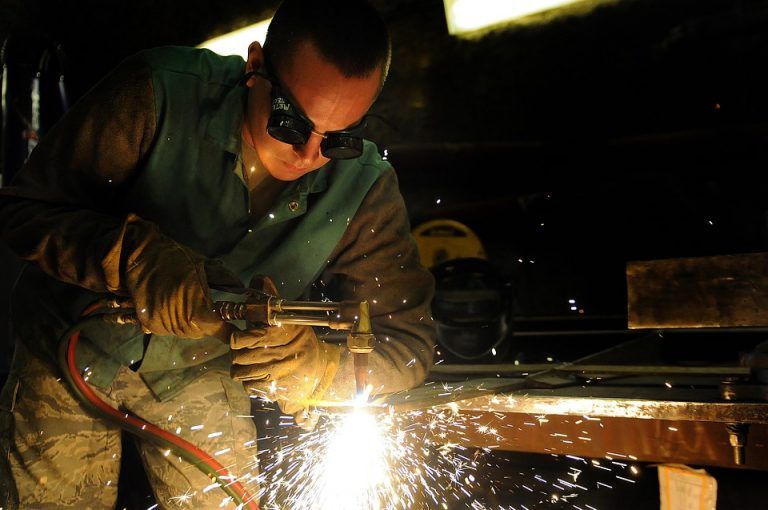

June 4, 2017
Eye injuries account for one-quarter of all welding injuries. This makes them by far the most common injury for welders, according to research from the Liberty Mutual Research Institute for Safety. Those most at risk for welding-related eye injuries are workers in industries that produce industrial and commercial machinery, computer equipment and fabricated metal products. Therefore, we will discuss the importance of safety glasses for welding.
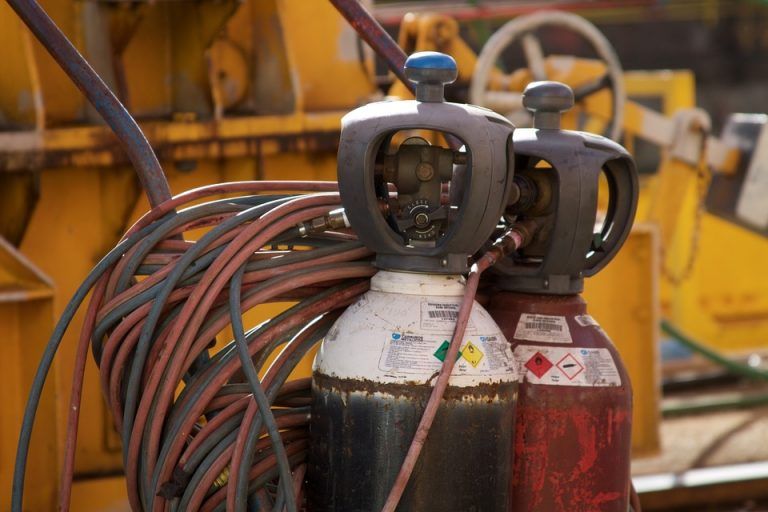

April 30, 2017
Following a regiment of appropriate and thorough maintenance procedures allows a welding machine to run safely and dependably for a long time. Improper, incomplete or totally neglected maintenance can not only result in equipment failure, but it can also lead to serious hazards including severe injury or even death. With some forethought and basic planning, welding machine maintenance is extremely easy.
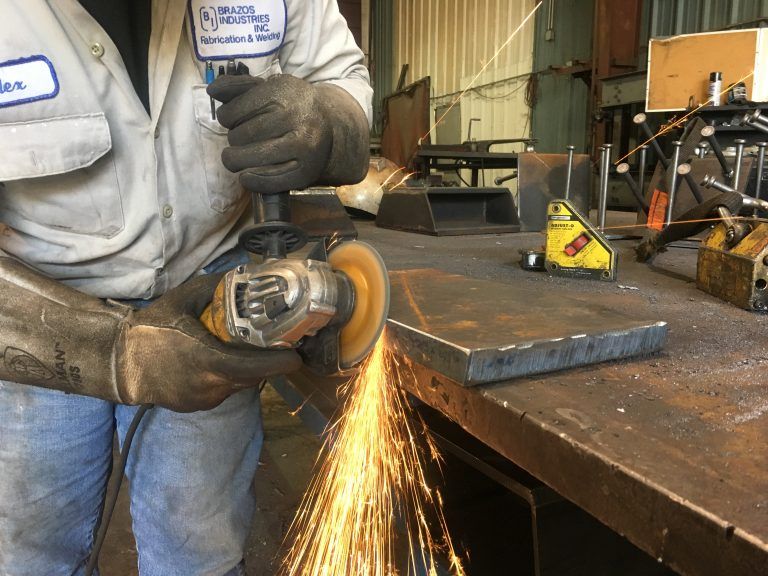

By localedge
•
March 5, 2017
A good weld begins with good preparation, and good weld preparation begins with a clean cut. However, cutting is an art that requires both skill and knowledge of how to select and utilize the best grinding wheel for the job. The type of grinding wheel to use for a given application depends largely on what material you are cutting. We will discuss using the right grinding wheel for the welding job.

February 5, 2017
You can fit oxy-fuel torches with a “Cutting Head” and use them to cut one solid piece of metal into two or more pieces. Lighting, adjusting and shutting down an oxygen-acetylene torch is easy, particularly when following to proper procedures. We will discuss properly adjusting the flames for the oxy-fuel cutting.
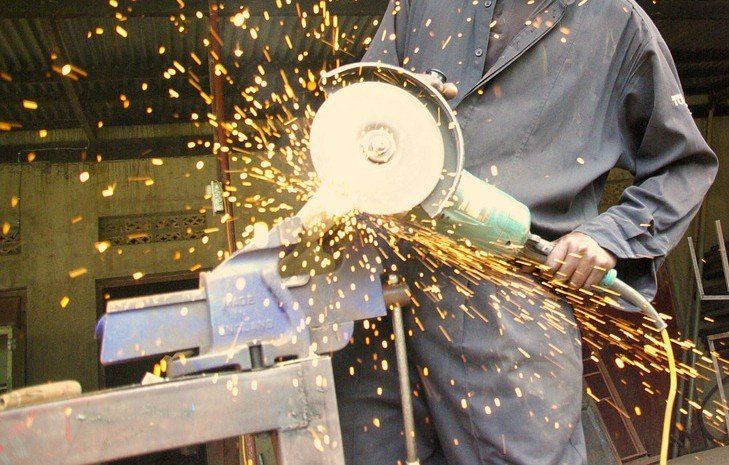

January 15, 2017
A basic component of any welder’s toolbox is a decent angle grinder. There are few tools more versatile than a grinder. However, not all grinders are equal. Therefore, trying to choose the right one can be difficult. We will discuss a few tips for choosing the right grinder size for the job.
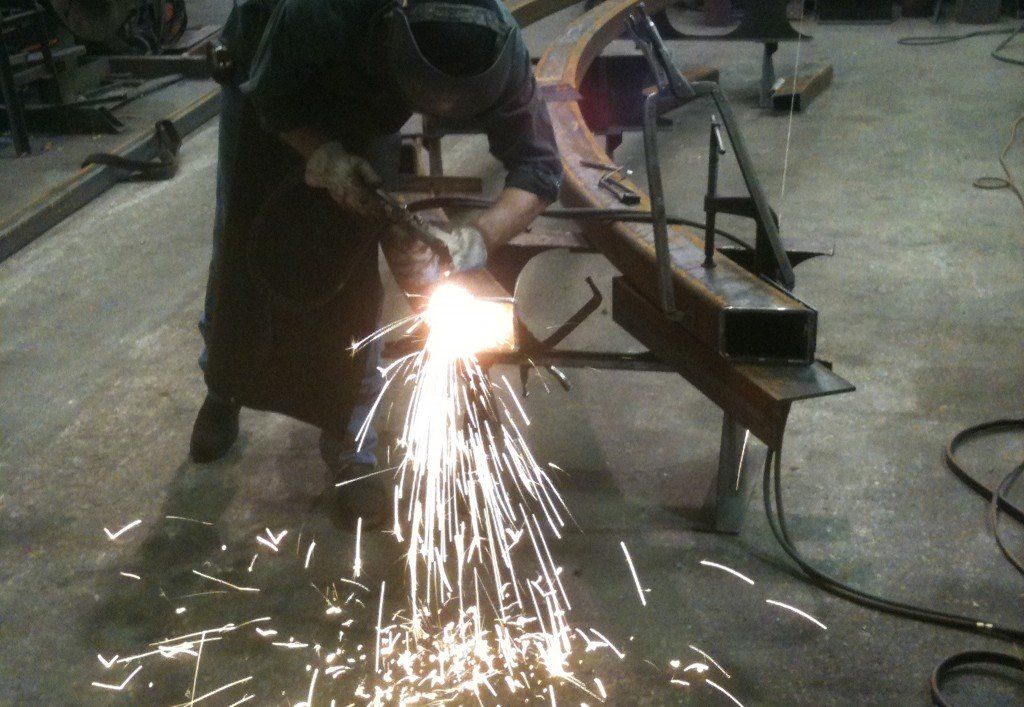

December 4, 2016
Selecting the right cutting or styling tool for the job means the difference between an average cut or a great cut. Therefore, it is important to choose carefully. It is critical to both performance and safety to choose the correct tip for the job. Here’s a simple step-by-step process for choosing the right cutting tip to ensure you deliver a great cut every time.